· Product Introduction
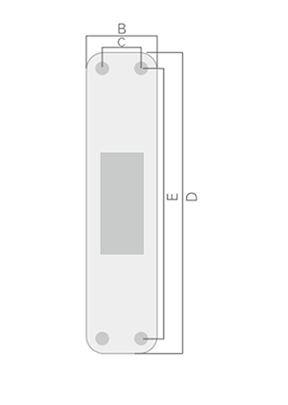
· Model
ZL10 |
B(mm) 77 | C(mm) 42 | D(mm) 155 | E(mm) 119 | Thickness ( mm ) 9+1.25N |
Max flowrate ( m3/h ) 4 |
Weight ( Kg ) 0.28+0.027N Design pressure ( Mpa) 3/4.5 |
We may modify and upgrade the parameters listed in the drawings and parameter tables without prior notice. The performance parameters and dimensional drawings are subject to order confirmation.
Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers (BPHEs) are integral components in HVAC systems, playing a crucial role in both heating and cooling processes. Here's how BPHEs are utilized in HVAC applications:
Efficient Heat Transfer: BPHEs offer high thermal efficiency due to their compact design and large surface area for heat exchange, which is ideal for HVAC systems where space is often limited .
Versatility: They are used in a wide range of applications within HVAC, including central heating, domestic hot water systems, ventilation, and air-conditioning installations .
Reliability: Manufactured to meet rigorous standards such as ASME, UL, PED, and EAC, ensuring durability and reliability in HVAC systems where consistent performance is required .
Flexibility in Design: BPHEs are available in various designs, such as 1- or 2-pass versions with different types of connections, allowing for easy integration into existing or new HVAC systems .
Low Operating Costs: With high heat transfer efficiency, BPHEs help maintain high thermal performance while keeping operating costs low, an essential factor for HVAC system owners .
Easy Maintenance: The user-friendly selection software and design of BPHEs make the selection and maintenance process straightforward, contributing to the ease of service in HVAC applications .
High Resistance to Temperature and Pressure: BPHEs are designed to resist high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for HVAC systems that may experience a range of operating conditions .
Applications in Chillers and Heat Pumps: In chillers and heat pump systems within HVAC, BPHEs serve as evaporators and condensers, facilitating the transfer of heat between the refrigerant and the surrounding air or water .



















