Product Introduction
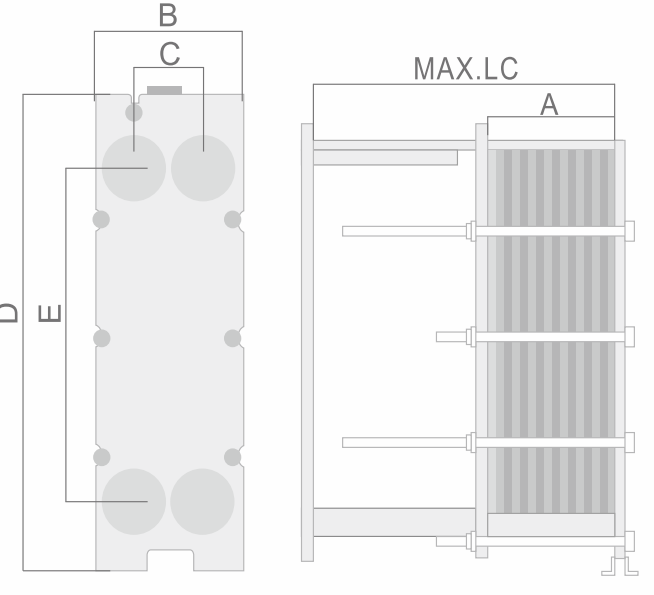
Model
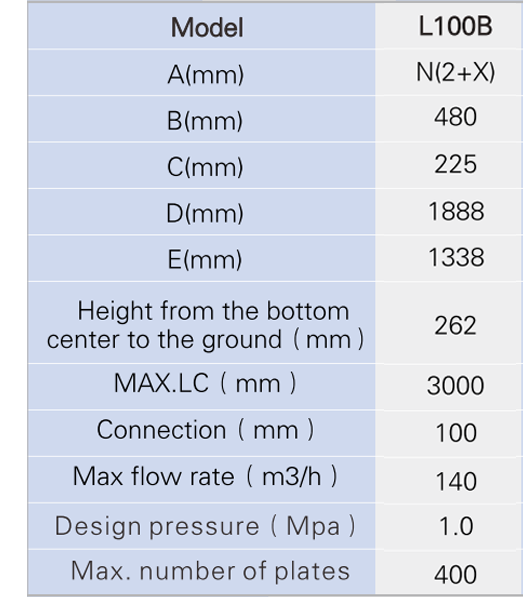
We may modify and upgrade the parameters listed in the drawings and parameter tables without prior notice. The performance parameters and dimensional drawings are subject to order confirmation.
Gasket plate heat exchangers, also known as plate-and-frame heat exchangers, are a type of heat exchanger that utilizes a series of plates separated by gaskets to transfer heat between two or more fluids. Here's an introduction to gasket plate heat exchangers:
Basic Structure:
Plates: The core of the heat exchanger consists of a series of thin, flat metal plates that are stacked together. These plates have a specific pattern of corrugations or channels that provide the flow paths for the fluids.
Gaskets: Between each pair of plates, there is a gasket that seals the plates together and prevents the fluids from mixing. The gaskets are made from materials that can withstand the temperatures and chemical properties of the fluids being heated or cooled.
Frames: The plates and gaskets are clamped together within a frame, which provides structural support and allows for easy disassembly for cleaning or maintenance.
Operation:
Fluids enter the heat exchanger through designated ports and flow through the channels created by the corrugated plates.
Heat is transferred between the fluids by conduction through the metal plates.
The fluids exit through separate ports, having undergone the desired temperature change.
Advantages:
Flexibility: Gasket plate heat exchangers can be easily disassembled for cleaning or replacement of gaskets, which is beneficial for applications involving fouling or corrosive fluids.
Customization: They can be tailored to specific applications by varying the number of plates, the type of gasket material, and the plate pattern.
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, including heating, cooling, pasteurization, and sterilization in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and chemical processing.
Ease of Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance are facilitated by the ease of disassembly.
Disadvantages:
Leakage Risk: Over time, gaskets can degrade or fail, leading to potential leaks between the fluids.
Pressure Limitations: The pressure rating of the heat exchanger is limited by the strength of the gaskets and the clamping force of the frame.
Space and Weight: Compared to brazed or welded plate heat exchangers, gasket plate heat exchangers can be larger and heavier for the same heat transfer duty.
Applications:
They are commonly used in applications where frequent cleaning or the ability to handle different types of fluids without cross-contamination is required.
They are also used in situations where the heat exchanger needs to be easily disassembled for maintenance or inspection.
Gasket plate heat exchangers offer a flexible and customizable solution for heat transfer applications where the ability to disassemble the unit for cleaning or maintenance is a priority. Despite some limitations, they remain a popular choice in many industries due to their versatility and adaptability.
























