Product Introduction
Model
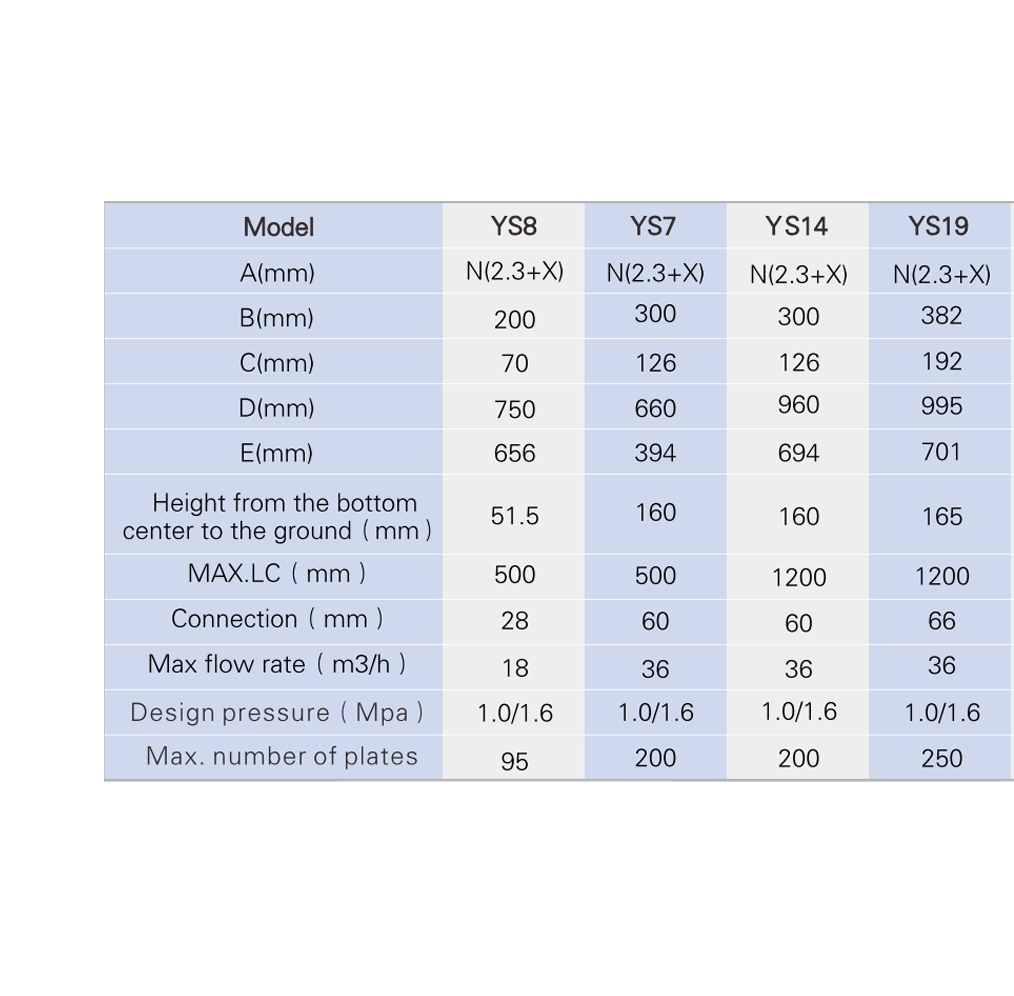
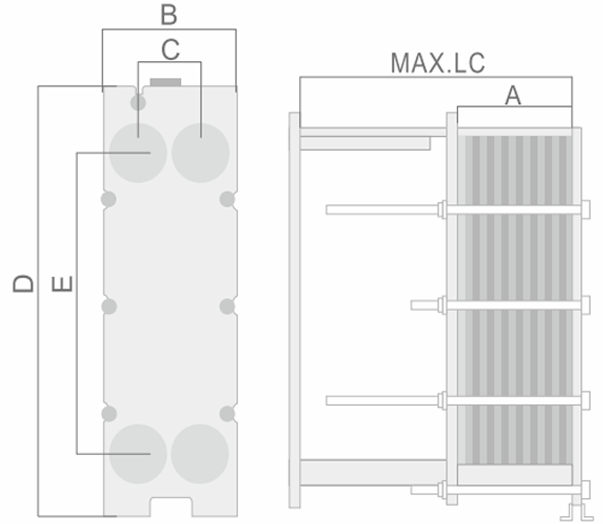
We may modify and upgrade the parameters listed in the drawings and parameter tables without prior notice. The performance parameters and dimensional drawings are subject to order confirmation.
Gasket heat exchangers, also known as plate-and-frame heat exchangers, are versatile and widely used in various industries for their adaptability and ease of maintenance. Here's a detailed look at gasket heat exchangers:
Structure and Components:
Frames: The frame holds the plates and gaskets together. It is typically made of steel or other strong materials.
Plates: These are thin, flat metal sheets that have a pattern of grooves or corrugations to create flow channels for the fluids. Plates are usually made from stainless steel, but other materials can be used depending on the application.
Gaskets: These are the sealing elements that sit between the plates and prevent the fluids from mixing. Gaskets are made from materials that can resist temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure.
Operation:
Fluids enter the heat exchanger through inlets and flow through the alternating channels created by the corrugated plates.
Heat is transferred between the fluids through the metal plates, which have a high thermal conductivity.
The fluids exit through separate outlets, having undergone the desired temperature change.
Advantages:
Customization: Gasket heat exchangers can be easily customized by adding or removing plates to meet specific heat transfer requirements.
Ease of Maintenance: Gaskets can be replaced without major disassembly, and the entire unit can be taken apart for cleaning or inspection.
Flexibility: They are suitable for a wide range of applications and can handle various types of fluids.
Reliability: With proper gasket selection and maintenance, these heat exchangers can provide reliable service.
























