Product Introduction
Model
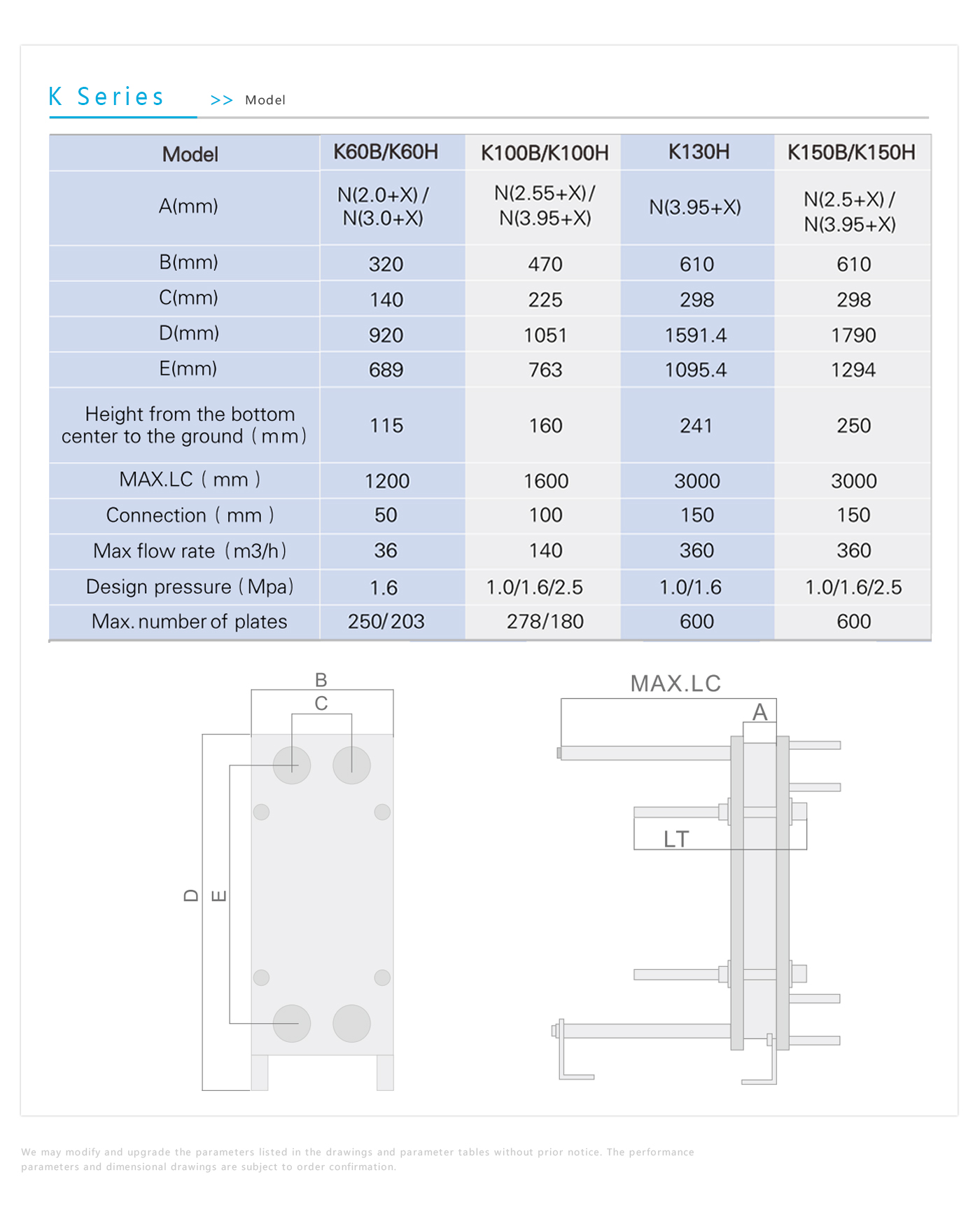
We may modify and upgrade the parameters listed in the drawings and parameter tables without prior notice. The performance parameters and dimensional drawings are subject to order confirmation.
Application
Gasket plate heat exchangers are widely used in central cooling systems due to their efficiency and versatility. Here's how gasket heat exchangers function in central cooling applications:
Heat Transfer: Gasket plate heat exchangers consist of a series of corrugated metal plates with portholes that allow two fluids to flow and exchange heat. The plates are fitted with gaskets that seal the channels and direct the fluids into alternate channels, promoting efficient heat transfer .
Space Efficiency: These heat exchangers are known for their compact design, requiring 20-50% less space compared to shell-and-tube units, making them ideal for applications where space is a constraint .
Energy Efficiency: Due to their high thermal efficiency, gasket plate heat exchangers can reduce the need for cooling media and allow for the use of smaller pumps, which consume less energy .
Customization: The number of plates and the design can be customized based on the flow rate, physical properties of the fluids, pressure drop, and temperature requirements .
Easy Maintenance: Gasket plate heat exchangers are easy to disassemble and clean, which helps in maintaining hygiene standards and prevents scale buildup .
Reliability: The use of gaskets allows for reliable sealing and the ability to handle a range of pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for various cooling applications .
Applications: They are used in a variety of central cooling applications, including HVAC systems, industrial processes, and even in marine environments where compact and efficient heat exchange is required .
Connection Types: Gasket plate heat exchangers offer various connection options such as compact flanges, external threads, and welding, which provide flexibility in installation and integration with existing systems .
Materials: Common materials used for the plates include AISI 304 and 316L stainless steel, which are suitable for a wide range of cooling media, including water and refrigerants .
Advantages Over Traditional Types: Gasket plate heat exchangers offer advantages such as lower energy consumption, less space requirement, and potentially lower maintenance compared to traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers .























