Product Introduction
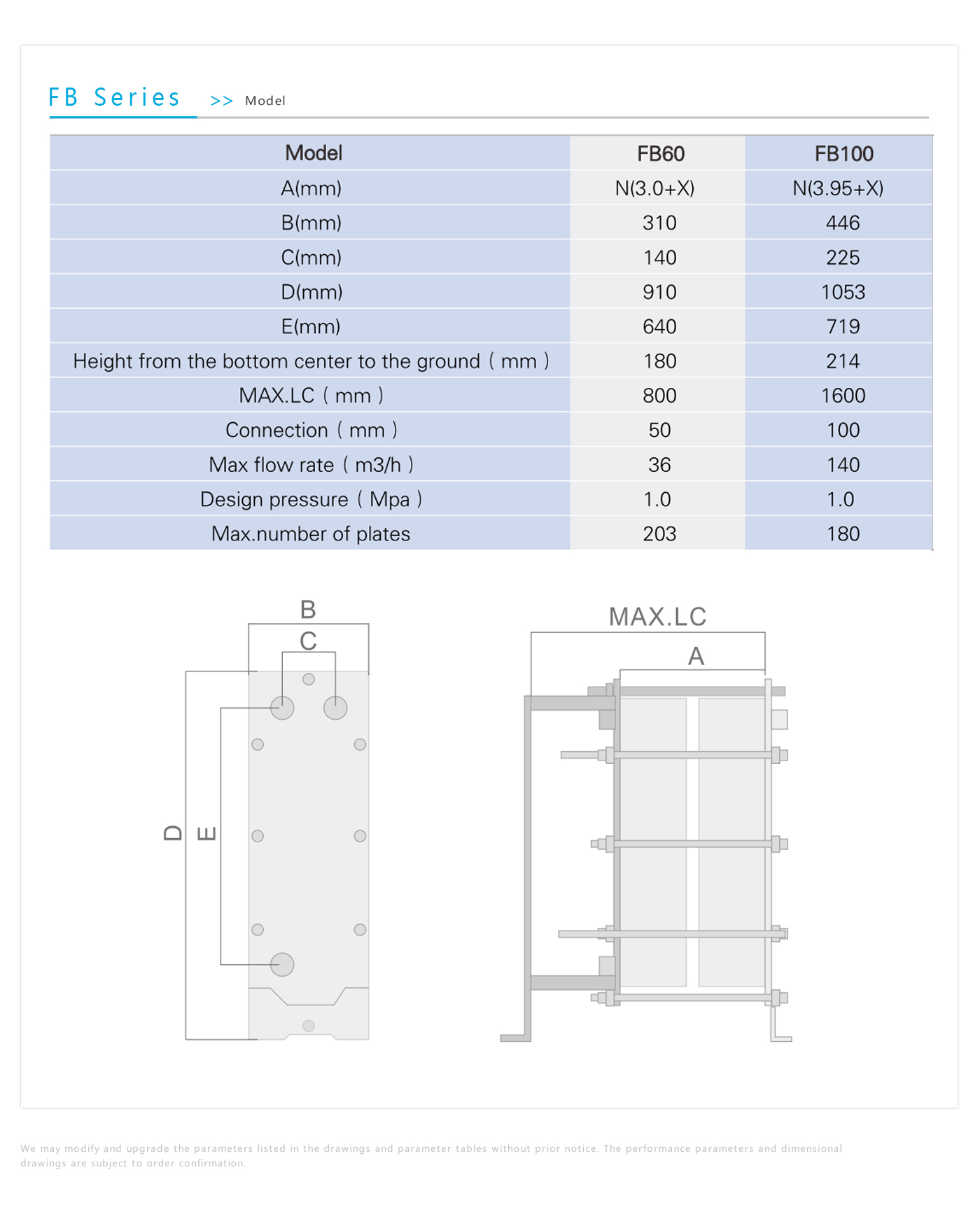
Gasket heat exchangers, also known as plate-and-frame heat exchangers, are engineered devices designed to transfer heat between different media without mixing them. They are widely used due to their flexibility, adaptability, and ease of maintenance. Here’s an overview of gasket heat exchangers:
Components:
Frames: The structural component that clamps the plates and gaskets together under pressure.
Plates: Thin, flat metal sheets with a pattern of grooves or corrugations that create the flow channels for the fluids. They are typically made from stainless steel but can also be made from other materials depending on the application.
Gaskets: Elastomeric seals that are placed between each plate to prevent leakage and ensure that the fluids do not mix. Gaskets are made from materials that can withstand the temperatures, pressures, and chemical properties of the fluids.
How They Work:
Fluids enter the heat exchanger through designated ports and flow through the channels formed by the corrugated plates.
Heat is transferred between the fluids by conduction through the metal plates, which have a large surface area in contact with the fluids.
The fluids exit through separate ports, having been heated or cooled as required.























