· Product Introduction
Brazed heat exchangers are integral components in HVAC systems for heating and cooling, as well as in refrigeration processes. Here's an overview of how they work in these applications:
HVAC Heating and Cooling: In HVAC systems, brazed plate heat exchangers (BPHEs) are used for efficient heat transfer with a compact design. They can be employed in various capacities such as air conditioning and process chillers, heat pumps, and gas boilers. The BPHEs offer benefits like being compact, easy to install, self-cleaning, requiring low levels of service and maintenance, and being gasket-free, which eliminates the risk of fluid intermixing and contamination .
Refrigeration: In refrigeration systems, brazed heat exchangers serve as condensers, evaporators, desuperheaters, and subcoolers. They are designed to provide efficient heat transfer, which is crucial for the performance of refrigeration systems. For instance, Alfa Laval's BPHEs are engineered to ensure the highest possible thermal performance within the smallest footprint, making them ideal for use with natural refrigerants due to their compact design, optimized plate design, and high design pressure .
Working Principle: Brazed plate heat exchangers consist of thin, corrugated stainless steel plates that are vacuum brazed together using copper or other filler materials. This process forms a self-contained unit without the need for gaskets or frame plates, resulting in a compact heat exchanger with high heat transfer efficiency and pressure resistance .
Applications in Refrigerant Systems: In refrigerant systems, brazed heat exchangers can be used in several ways, such as:
As evaporators in direct expansion (DX) systems where refrigerant evaporates and absorbs heat, leading to cooling.
As condensers where the hot refrigerant gas is cooled and condensed into a liquid state.
As desuperheaters to remove additional heat from the superheated refrigerant vapor before it enters the compressor.
As subcoolers to reduce the temperature of the liquid refrigerant below its saturation temperature, enhancing system efficiency .
Benefits: The benefits of using brazed heat exchangers in HVAC and refrigeration systems include their lightweight construction, which offers greater thermal efficiency and a smaller footprint compared to traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers. They also provide high compression resistance, robust construction, and high corrosion resistance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications
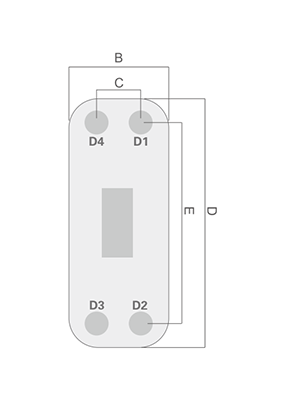
· Model
ZL200(E) |
B(mm) 320 | C(mm) 207 | D(mm) 742 | E(mm) 624 | Thickness ( mm ) 14+2.7N |
Max flowrate ( m3/h ) 100 |
Weight ( Kg ) 13+0.67N Design pressure ( Mpa) 1.5/2.1/3 |
We may modify and upgrade the parameters listed in the drawings and parameter tables without prior notice. The performance parameters and dimensional drawings are subject to order confirmation.

































